There exists an inevitable relationship between marketing and accounting. Marketers have been using accounting for a very long time.
Even one of the components of the marketing mix, pricing, is decided on the basis of accounting. Apart from this, deciding upon various decisions like – what alternatives and strategies to follow, product range decisions, sales and demand forecasting, preparing budgets, performance evaluation and the list goes on if I were to explain the application and importance of management accounting to the marketing department.
As budding marketers, you need to have a strong understanding of accounting concepts to be a successful marketer. But you don't need to worry if you haven't paid attention to accounting classes or didn't understand the concepts! This article will give you a basic understanding of accounting concepts and the role of finance in marketing. Let us start by understanding the role played by accounting for marketers!
How Does Accounting Relate to Marketing?
The following points will help you to understand various marketing activities where accounting knowledge is required:
Pricing
Pricing is a broad component and involves many things like selecting pricing objectives, determining demand, estimating costs, analyzing competitors' prices, deciding a pricing method etc. Marketers should have a clear understanding of various costs involved to estimate an accurate price for consumers.
Sales Planning
Marketers need to plan sales activities frequently. If you are going to sell your product in a new territory, then you as a marketer need to forecast sales and demand for that area. You need to know how to estimate the sales as all the other marketing activities depends upon how accurately you estimate the sales forecast.
Preparing Budgets
Marketers have to prepare monthly, quarterly and yearly budgets for various activities like advertising, sales, promotion etc. Sales forecast, demand forecast are vital components in preparing budgets.
Evaluation of Multiple Alternatives
As a marketer, you will come across various alternatives in your day-to-day operations like - Whether to introduce a different product offering or not? Expand sales workforce or increase advertising? Continue serving a market segment or not? Capture new markets or not? All these decisions are very crucial and cannot be taken in "blue skies". The accounting will help you to evaluate all these options using financial analysis and take a mindful decision.
Marketing Control
It is the process to evaluate the effectiveness of various marketing activities and operations. Further changes and adjustments are made according to the performance. This involves the use of variance analysis, sales-to-expense ratios etc.
P&L Responsibility
The revenues for marketing department are increasing with time due to fast pacing digital transformation. It is no longer a cost center but is being given P&L responsibility. A marketing blog of Gartner mentions - Scott Davis, author of "The Shift: The Transformation of Today's Marketers into Tomorrow's Growth Leaders", says that for senior marketers to become visionary leaders, a P&L mindset is a requisite. The P&L is where marketing strategies and tactics will ultimately be measured for their effect on the bottom line.
All the above points clearly show the importance of accounting for marketers; most of the tools and analysis methods are based only on cost accounting. I hope that by now, you have understood how does accounting relate to marketing and why accounting for marketers!
Now we can get on the ground to learn accounting for marketers. Read further to get a basic understanding of accounting concepts!
Accounting for Marketers
Although accounting includes a lot of concepts but the following points will give you a crux of all the basic concepts along with examples that you must know as a marketing student and a future CMO:
Understanding Costs
To decide your product's pricing, you should clearly understand your product's various cost components. Demand will set the ceiling for your price and costs will set the floor. You must have a clear understanding of both the ceiling and the floor to rule the entire pricing game!
The different types of costs are:
Fixed Costs:
Employees salaries, rent, electricity bill, interest paid; have you noticed anything common with all these costs? Yes, they all do not vary with the level of production or sales revenue. If you sell 100 units or 10 units, you have to pay the rent of your factory! These are also called as overhead costs.
Variable Costs:
Apple incurs the cost of plastic, microprocessors, chips, display and other electronics and packaging to produce an iPhone. These are the costs which depend upon the number of units produced. These are called variable costs.
The sum of variable costs and fixed costs constitute Total Costs.
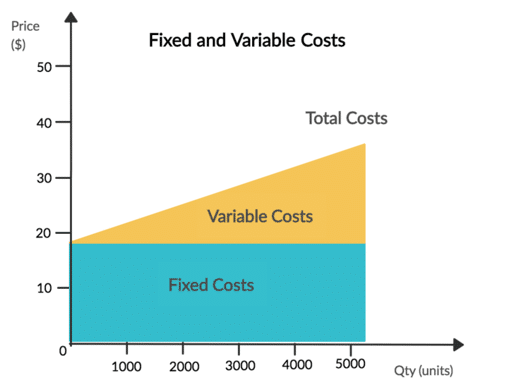
Source: boycewire
Average Costs:
Average cost will give you the per-unit costs of producing an iPhone for apple. It can be calculated by:
Average Costs = Total costs / number of units produced
The below curve gives you the various short-run average cost curve for a CD manufacturing company. The average cost curves are plotted by taking the average cost per unit corresponding to different quantity levels. As a manager, you will decide to produce the number of units having the lowest average cost per unit.
If you join the lowest point of all the short-run cost curves – A, B, C, D; you will get the long-run average cost curve. You should produce 30 units of CDs in the long run because the average cost per unit is minimum at this point at Rs. 5 per CD.
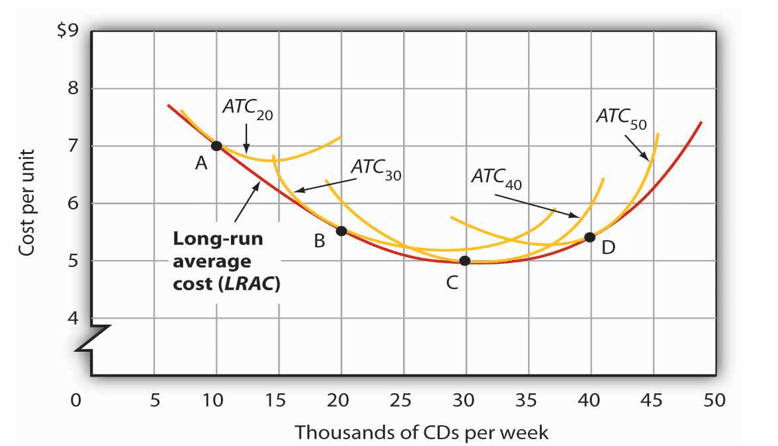
Source: Lumen Learning
Break-Even Analysis
As a marketer, you must analyze how many units you should sell to cover your fixed costs. Now, you must be thinking why I am saying at least fixed costs and not the entire costs? Read further to understand!
Before this, let us understand another important concept of Contribution. Sales price minus variable cost is equal to the contribution margin of the product. It is used to decide the price level; any price below contribution is unacceptable because the price is not even able to cover the variable portion of the total cost.
Contribution per unit = Sales price per unit – variable cost per unit
Now, we are all set to understand what is break-even analysis!
Break-even point is used to calculate, as a marketer, how many units you should sell in a given period to cover the incurred fixed costs. Now, coming to the question - why only fixed costs?
Consider you are not manufacturing any number of units for a week. Now, irrespective of whether you produce or not you still have to pay for the electricity bill, you still have to pay your permanent workers' salaries, you still need to pay your factory rent. As a rational sales manager, you will think that you must sell this number of units to make your company survive in a worst-case scenario. The formula for calculating the break-even output level is given below.
Break-even point = Fixed Cost / Contribution per unit
Remember, break-even point tells you about the minimum number of units you should sell to survive the business.
Let us understand graphically as well.
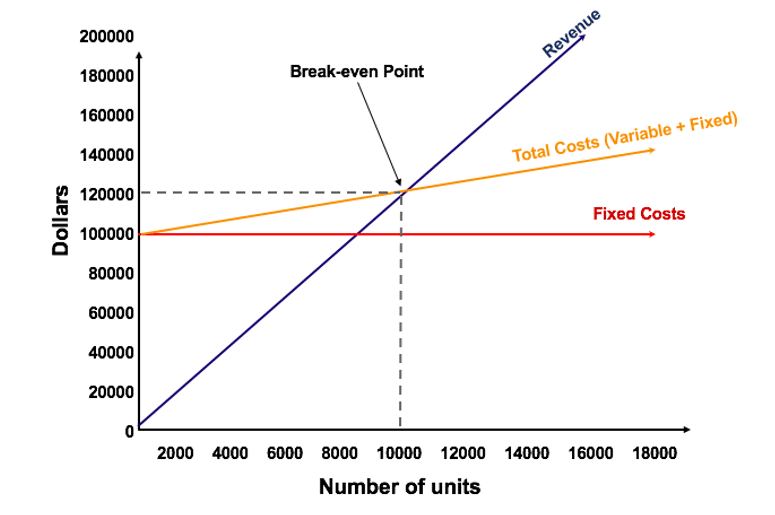
Source: Corporate Finance Institute
Suppose you are a sales manager of KitKat India and you need to decide the break-even point for KitKat. Here, the fixed cost is $100,000 depicted by a straight line. The variable cost is $2 per unit. The selling price of a unit of chocolate is $12. A 45 degrees line depicts the revenue as it increases proportionately with the number of units sold.
Now, Contribution = 12 – 2 = $10
Break-even point = 1,000,000 / 10 = 10,000 units of KitKat
Here, you can notice that total costs are equal to revenue at the break-even level of output. Hence it is a no-profit and no-loss situation.
If you produce below 10,000 units, you will incur a loss. If you produce above 10,000 units, you will start earning profits.
Budget Preparation
As a marketing team member, you need to prepare budgets for promotion activities, advertising activities, and sales activities. The sales budget is one of the essential budgets out of all and lays the basis for other budgets.
A budget is a detailed plan of operations prepared in advance. A sales budget gives the forecasted sales amount for the coming period. The budget also acts as a target of sales figure to be achieved in the coming period. It is prepared by forecasting the future sales based on the past figures and trends.
Suppose you are a sales manager of Incredibles Industries Ltd.; it is a T-shirt manufacturing company. You need to prepare a sales budget for men and women T-shirts in two different areas. As a first step, you need to forecast two components – Volume and Price.
Sales volume or units can be forecasted using various methods based on the past figures of sales. One of the ways is Compound annual growth rate (CAGR).
CAGR gives you the growth rate over the years. Here in the picture below, the CAGR will provide you with the growth rate in sales from 2010 to 2014. You can forecast future sales by multiplying the current sales amount with (1+ CAGR). The formula for CAGR is given in the below image.
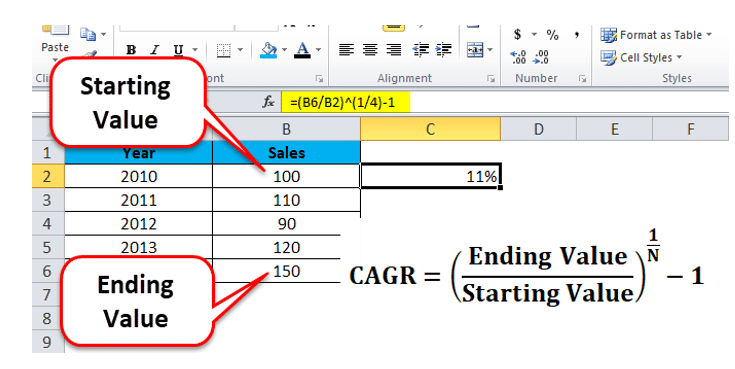
Source: eduCBA
The price can either be taken the same or estimated according to the product's cost and demand. After this, you can easily prepare a sales budget in the given format. As a sales manager, you also need to compare the actual sales with budgeted sales to calculate the variance and forecast for the future period accordingly.
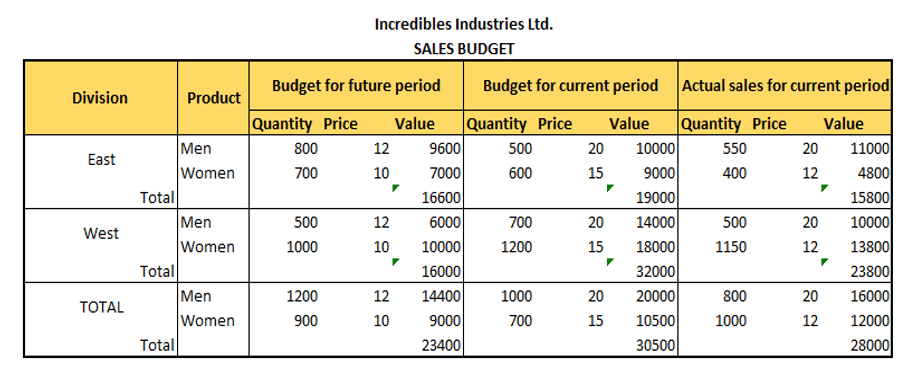
Sales-Variance Analysis
Suppose, as a toy company's marketing manager, you decided to sell 4000 toys at Rs. 10 each to get a revenue of Rs. 40,000. But actual sales were 3000 toys at Rs. 9 and the total revenue earned was Rs. 27000.
Now, you can observe the deviation in the actual revenue from the targeted revenue. You need to do the variance analysis, as a marketing manager, to capture this deviation. To do the analysis, you must wonder how much difference is due to price and how much is due to volume! This analysis is nothing but sales-variance analysis, i.e., analyzing the actual sales with the targeted sales.
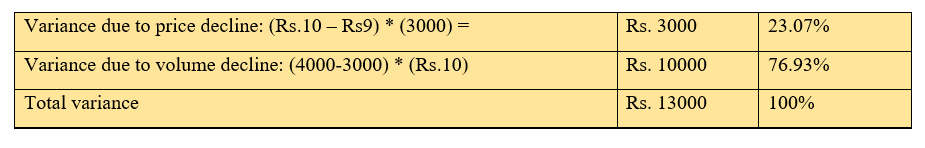
The analysis will help you understand that more variance is due to volume decline, and it requires much more attention to control the variance.
Expense-to-Sales Analysis
Marketing returns are one of the most difficult to identify and measure. But it does not mean that you should spend the money on marketing operations based on your intuition. Marketing expenses should remain in certain limits. For that, you first need to calculate the advertising expense-to-sales ratio, and then you can easily analyze the fluctuations in expenses at frequent intervals using Control Charts. Control charts portray the fluctuations within and outside the permissible or average limit.
Suppose you are an advertising head of Nestle and you have to analyze fluctuations of the advertising expenses. You will calculate the advertising-expense to sales ratio using the formula given below.
Expense to sales ratio = Expense (Advertising) / Sales
Then you will plot the ratio for different time periods on the control chart. The chart contains three lines to analyze the fluctuations:
- Upper Limit
- Desired level
- Lower limit
The more the points are near the middle line, i.e., the desired level, the better it is. Now, the control chart for your advertising department's expenses is given below. You can easily notice that usually, the ratio varies between 8 % to 12%. But in the current period, it is above 12%, which is above the upper limit.
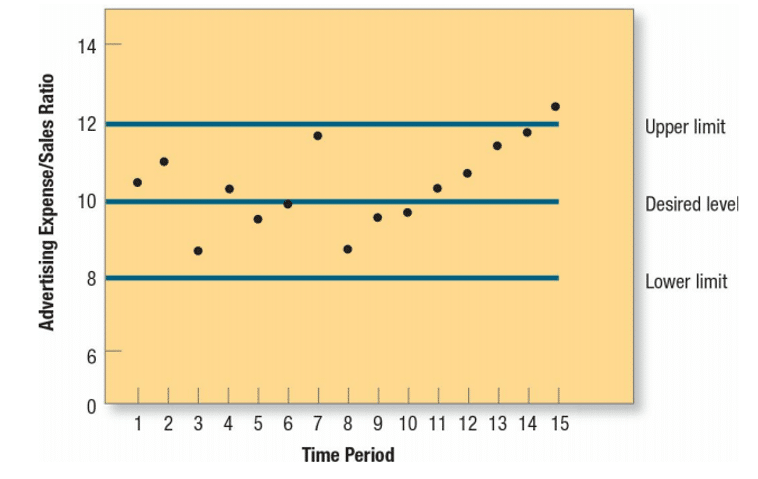
Source: Marketing Management15E, Philip Kotler, Kevin Lane Keller
Now, as the head of the advertising department, you can think of two possibilities:
- Either it is a rare event, and nestle has a reasonable expense control or
- Something is not right and you have to find the cause
I hope you must have got a basic understanding of accounting as a nurturing marketing student by now. You must have noticed that marketing is incomplete without accounting. Thus, indicating the importance of cost accounting in marketing!
Conclusion
- Accounting plays a vital role in various marketing activities like deciding the price, sales planning, preparing budgets, and evaluating multiple alternatives and marketing controls.
- Understanding costs are significant to decide the price. The different types of costs are fixed cost, variable cost, average cost.
- Break-even analysis helps in knowing the minimum number of units you need to produce to cover the fixed costs.
- At the break-even level of output, there are no profits and no losses.
- Marketers need to prepare budgets frequently using various forecasting methods; one of them is CAGR.
- The sales-variance analysis helps to understand whether the sales variation is because of price or volume.
- The Control chart is a tool used to analyze the fluctuations in the various marketing activities' expenses.