
Price! One of the most important 4Ps of the marketing mix. Although very analytical in nature, price is not the most favorite element of many, and I am one of them. But when I read about the price adaptation strategies in marketing as a research to write the article, turns out it is quite interesting.
Adapting the price that can bring the most customers to buy your product can be competitively advantageous.
Read on to know more about the price adaptation strategies with examples that can help you as a marketer.
Price Adaptation Strategies
Price is not only an element that displays the value of the product; it is more. It can generate interest among customers and is a great way to do promotion.
As a good marketer, you should understand the changing market's nuances and changing consumer behaviour and come up with pricing strategies that can best suit your customer. Understanding price adaptation strategies can help you do that.
Let us see what are the various approaches to pricing, along with some interesting examples.
Geographical Pricing
Geographical Pricing is a way of pricing your product depending upon the location of your buyer. You can sell your product at different prices in different locations.
For example, a product being sold in India at ₹100 can be charged at $2.47 (₹180) in the US. Not only price can differ within countries, but it can also vary within cities or districts.
Geographical pricing is affected by the following aspects:
- Transportation or shipping cost
- Consumption levels of the consumers
- Price sensitivity of the consumers
- Presence of competitors
- Exchange rates
Example: Coca Cola
Coca Cola is a well-known brand all over India. A 600 ml bottle of Coca Cola is priced at ₹38. However, the Indian rural market is far more different than the urban market in terms of purchasing power and consumption levels. To cater to the needs of India's rural market, Coca Cola adopted a geographical pricing strategy and priced a 200 ml bottle for ₹5.

Source: chirayusharma
Promotional Pricing
A promotional price adaptation strategy is the approach of reducing the price of the product on a temporary basis to attract customers to buy your product.
The types of promotional price adaptation strategy are as follows:
- Loss-leader pricing: This pricing is mainly adapted to get consumers in the store and increase brand awareness. In this case, the prices of the products might be even lower than the cost of their production, but the strategy is such that the lower price of the product is what bring consumers in the store and they buy in volume. Look at the following video to understand more about loss-leader pricing.
- Special Event Pricing: Remember headlines like “This Diwali Season, get everything at 50% off” or “Enjoy a candlelight dinner with your Valentine under just ₹999”. This pricing is changed or adapted based on any special event to bring customer traffic.
- Special Customer Pricing: This is based on the type of customers. Generally, loyal customers are said to gain the most benefits. For example, a gold card member at Pantaloons might get larger discounts than a green cardmember.
- Cash Rebates: This pricing includes giving refunds to customers who buy from you within a specified time. For example, you give a 20% discount to the customer at the time of purchase of a cell-phone.
- Low-Interest Financing: Here, you do not cut the price of your product, but you give low-interest financing. An example of this is smartphone companies providing easy EMIs with a low-interest rate.
- Warranties and Service Contracts: You can increase your sales by giving extended, low cost or free warranties and service contracts to the customers. Look at the image below for example,

Source: Generxgenerators.com
- Psychological discounting: Her you play with the customer’s mind a little by excessively increasing the price of the product and then giving heavy discounts. The following image will give you an idea of psychological discounting.

Price Discounts and allowances
You can give discounts and allowance on your product to make it more affordable to the consumers or make the product more competitive in the market.
Discounts and allowances can lead to early payments, bulk purchases, and off-season purchases. This price adaptation strategy is also very useful in increasing the brand or product awareness, increasing consumer traffic and pushing sales.
There are various types of price discount and allowances can you can adapt as your price adaptation strategy which are as follows along with examples:
- Quantity Discounts: You may offer a quantity discount to your buyer who buys in large volumes. Remember asking for a discount on 2 kg apples like “Bhaiya 100 rupaiye lelo 2 kg apple lugi (I will give 100rs for 2kg rather than 70rs for 1kg)”, quantity discount works like that.
- Volume purchases reduce the unit cost of manufacturing, marketing and transporting.
Example of Quantity Discount is as follows:

Source:coredna.com
- Functional Discounts: The discounts you give to various members across the distribution channel are called functional discounts. They are also called as trade discounts.
In simple terms, functional discounts are those that you give to a distributor or a retailer as incentives to buy from you.
- Seasonal Discounts: That discounts you might give to your buyers to increase sales in the off-season is called a seasonal discount.
For example, a “Happy Hour”. Restaurants give discounts during lunch hours or tea-time hours when traffic to the restaurant is at the least.

Source:dominos.com
- Cash Discounts: The discount that you might give to a buyer who pays all bills punctually. Take a look at your monthly electricity bill; you will see the following column in there.
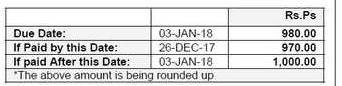
I hope the image makes it quite clear what discount price adaptation strategy means.
Discriminatory Pricing
Another form of price adaptation strategy is discriminatory pricing. In this, you will be charging the same product or service at different prices depending upon the consumer segment, channel, form of the product, location etc.
By looking at the types of discriminatory pricing below, you will be better able to understand the discriminatory price adaptation strategy.
- Customer Segment Pricing: The practice of charging different customer segments, different pricing is called as customer segment pricing. These can be based on gender, age, income etc. For example, look at the image given below, it is purely a gender-based customer segment pricing, where discounts are offered only to the ladies.

Source:inspirebangkok.com
- Product-form Pricing: Pricing based on the different versions or forms of the product is called product-form pricing. For example, a 100gm bottle of Nescafe Classic coffee is priced at ₹290, but the same coffee is priced at ₹10 for a 100mg sachet.
- Image Pricing: Giving different prices based on image differences is called image pricing. For example, a company selling something called as moisturizer classic for ₹100, and the same product called as moisturizer crème for ₹200.
- Channel Pricing: Prices might differ across various channels such as offline or online, retailer or wholesaler. For example, when you visit a restaurant, a dish would be priced higher than the same dish ordered on Zomato.
- Location Pricing: Prices might differ based on location even if the cost of production of the product is the same. An example of this would be, movie theatres, where prices of the seats differ based on their location such that seats in the front row are priced much lower than the seats at the back of the theatre.
- Time Pricing: Ever observed that the price of roses goes up like crazy during Valentines, or the concert tickets priced lowered for those who buy one week just after the launch of the tickets. Here, prices are dependent on timing, the timing of when you buy the product.
Conclusion
- Price adaptation strategies can help you bring traffic to your store and increase brand awareness
- Geographical pricing is affected by transportation or shipping cost, consumption levels, price sensitivity of the consumers, presence of competitors and exchange rates
- A promotional price adaptation strategy helps in attracting customers to buy your product by reducing your price temporarily
- Discounts and allowances can lead to early payments, bulk purchases, and off-season purchases
- Discriminatory pricing is price discrimination depending upon the consumer segment, channel, form of the product, location etc.







very nice information