I have received several mails from MBA students and businesspersons asking me for the ideal business strategy for their projects and businesses for when they need to go international. This was because my last article on 5 Modes of Entry into International Business really gave them a headway into what strategy they should adopt. And that's when they asked me, what is transnational strategy in international business?
Well, today I want to tell you about a certain international business strategy called the Transnational Strategy which has worked perfectly for several companies.
I will also touch on the other business strategies that many organizations have employed and they have worked too. It will largely depend on the business you are working on, or the products and services that you offer.
What is Transnational Strategy?
A transnational strategy is simply a plan of action whereby a business decides to conduct its activities across international borders. This strategy is invested in overseas operations and assets, connecting them to every nation in which the company operates.
This strategy presents the centralization benefits that are given by a global strategy. Transnational business strategy is, however, distinct from multinational, international, and global business strategies.

Case Analysis Blueprint Course
Use marketing strategies and frameworks like these to solve business case studies with ease
Strategies like the Transnational strategy are a crucial part of global go-to-market plans. Get to know how to analyze a marketing case study comprehensively in just 5 slides. Which means that the next time you need to analyze a case, you know exactly how to ace the case
International Business Strategies
It is first crucial that you understand what these different international business strategies entail before I can explain further on the transnational business strategy.
International Strategy
An international strategy for business places its primary attention on the exports and imports market. The company, however, remains in its country of operation without establishing branches in other countries.
Here the company makes the necessary arrangements for supplying goods to customers in overseas countries and for imports. It ships products to overseas clients depending on the demand and supply logistics.
You can consider large wine producers from Italy and France to be ideal examples for firms applying an international business strategy. Their main aim is for their products to reach as many customers as possible all over the world.
Multi-domestic Strategy
Multi-domestic strategy is whereby the organization concentrates more on the needs of the local markets, its responsiveness, preferences, demands, and such issues in a given region of operation. We should understand that such a company will also invest in foreign countries, but their main emphasis is on customers and their needs.
These companies practicing multi-domestic strategy are known to sacrifice global efficiency and integration to achieve higher local responsiveness.
Nestle is a perfect example of a company employing multi-domestic strategy. The firm uses a specific sales approach and marketing for every market it operates in. The organization also adapts different products for each market according to consumer preferences.
Global Strategy
Companies employing global strategy prioritize global integration. Such a company is only concerned with going global and covering as many nations as possible. To such a company, local responsiveness is not much of a priority, meaning that they will not differentiate their products and services in different regions as you would reckon.
The global strategy has the company offering the same service or product and marketing strategy across all the nations and regions it touches.
When looking at examples for global companies, I cannot fail to mention pharmaceutical companies like Pfizer. The subsidiaries mainly depend on the parent company for supplies and management structures, logistics etc.
Transnational Strategy Examples
A transnational strategy, however, aims at ranking high in both local responsiveness and global integration. This strategy looks at scooping the benefits that come with operating in multiple countries.
Transnational companies as we know, aim at expanding their sales, lowering their production costs, and also attain economies of scale. These companies have headquarters and organizational structures that are decentralized in the nations they operate in.
The size and complexity of how the different sites relate depend on the business model that the company chose. The level of influence by the central office is also different in transnational companies.
I want you to note that uniform business technologies and policies are lucrative for the transnational business strategy, but again you have to give the other branches sufficient capacity and space to accommodate the business policies in a foreign operation.
Unilever makes a good example of a transnational business model. Its subsidiaries are given strategic roles to play by the parent company and help determine the customer wants. These subsidiaries also function as centers of excellence for the company.

Unilever's Product Portfolio around the world. Source: Dividend.com
The main aim of transnational companies is to maximize overall corporate performance via synchronizing markets and resources worldwide.
What is the transnational model?
From the transnational definition, you are aware by now that it is a company looking to dig deep into other countries' markets and achieve economies of scale from the same. Unlike a global strategy, the transnational business strategy has two main functions as I had stated earlier, and they include:
- High local responsiveness
- High global integration
On the basis of these two parameters of any international strategy, I have mapped each of the four strategies, as shown below.
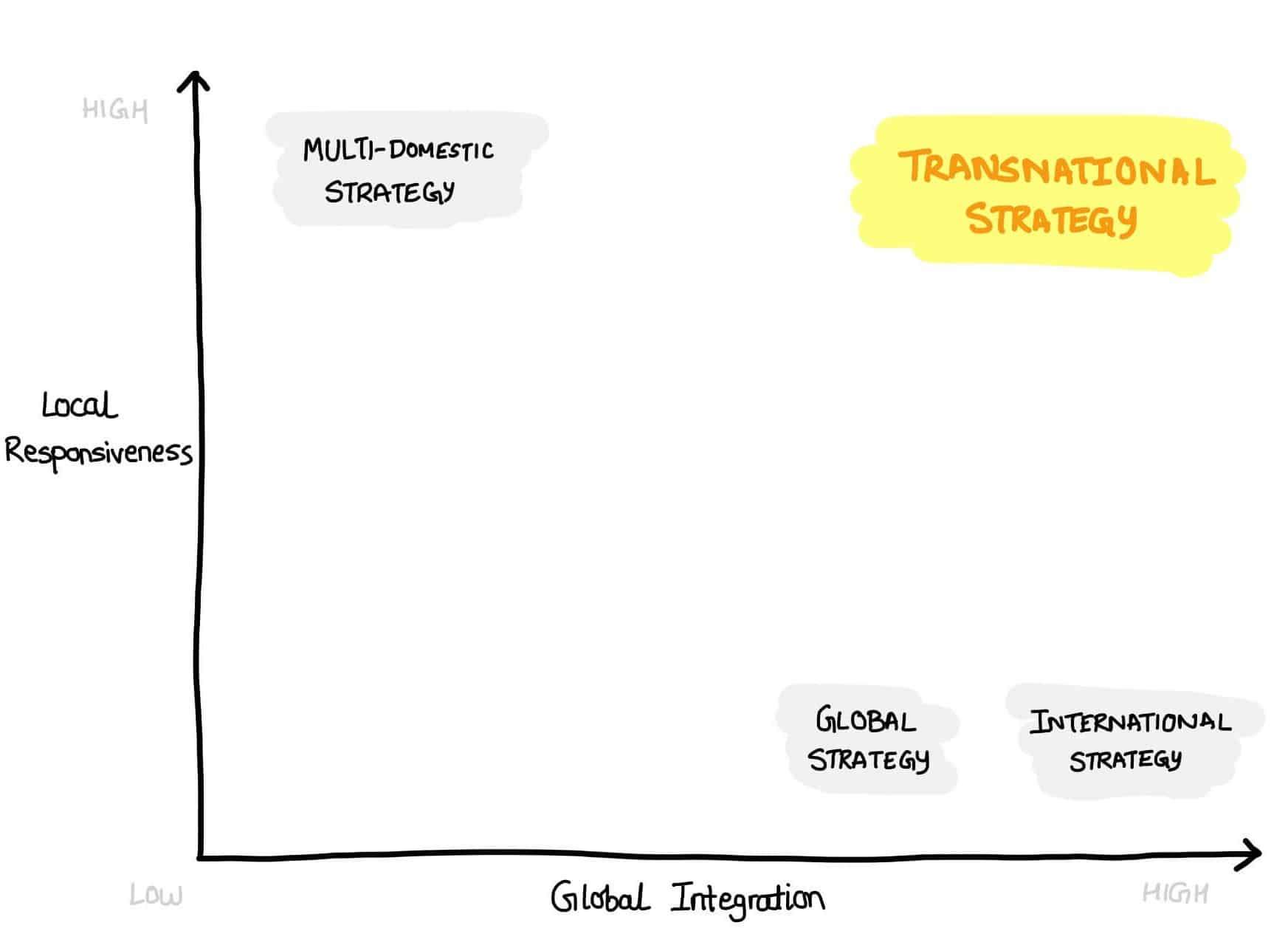
Two striking features of this arrangement are that; (i) the transnational strategy is high in both the parameters and, (ii) an international strategy would be considered higher in global integration than the global strategy as having a setup in just one country unifies the experience.
High Local Responsiveness
Transnational companies look into details of everything about the local markets in which they operate. They assess the needs of the local customers and their demands and attend to them accordingly.
Consider a good example here; an organization could be supplying one global service or product that they offer in all their branches. Still, they create additional services and products that are specific to the market they operate in. That is what happens with a transnational strategy for business.
The other issue you ought to comprehend is that in as much as these companies have a global marketing strategy and branding, the company will tailor its messaging, communication and campaigns depending on the area of operation.
These companies are always mindful of the local language, lifestyles, culture, unlike the global strategy, which only looks at selling their products to more foreign countries. The transnational business strategy ensures that what they are marketing aligns with the local language and culture of that specific region.
In the multi-domestic strategy, when creating the marketing content, full autonomy is given to the regional managers. The case is different in transnational corporations where the local branches are given the liberty to translate the organization's global message to the locally used language having the consumer preferences and cultural norms in mind.
In short as things stand, transnational business strategy balances efficiency and global standardization, having the ability to tailor the marketing, services, and products according to the local markets.
High Global Integration
Companies employing this strategy typically have a head office and a centralized management staff that oversees all the international operations. With a multi-domestic strategy, the subsidiaries are almost totally independent in every region. However, with a transnational strategy, all the subsidiaries are dependent on one central office.
Some organizations give more autonomy to some local subsidiaries than others, but the general feeling is to have high integration across every branch worldwide.
I must mention that, just like the global strategy, these transnational companies remain standardized all through the regions it operates to maintain lower costs and efficiency. Every branch of the transnational strategy typically follows a laid-out marketing strategy from the central office, and it runs on guidelines set by the central managerial team.
Transnational Strategy Advantages
1. The main advantage of this business model is that it is more economical than a multi-domestic strategy. That is because it advocates for efficiency and global standardization. Resources are as centralized as possible in a transnational business strategy meaning that it becomes efficient in cutting the production costs.
2. The other advantage is the deeper penetration in local markets. Multi-domestic strategy also enjoys this advantage, but companies employing international strategy and global strategy may have a hard time reverberating with local consumers.

Case Analysis Blueprint Course
Use marketing strategies and frameworks like these to solve business case studies with ease
Strategies like the Transnational strategy are a crucial part of global go-to-market plans. Get to know how to analyze a marketing case study comprehensively in just 5 slides. Which means that the next time you need to analyze a case, you know exactly how to ace the case
Final Thoughts
The transnational strategy can be very beneficial to a company if done the correct way. However, it may not be for every business in as much as it has two positive elements, which are high responsiveness and high integration.
Before deciding on which type of strategy of the business to employ, whether global strategy international strategy or multi-domestic strategy, it is crucial that you first assess the advantages of each and the risks they carry with them.