
Sales forecasting is only for salesmen.
Is it?
If you believe in that, then let me tell you that is incorrect. The fact is, selling is the responsibility of the brand manager more than it is of the salesmen.
The salesman’s primary responsibility is customer relations and customer management. If you’re the brand manager and the sales are bad, your boss isn’t going to catch the salesman. She is going to catch you!
So let me dispel this myth right up – the responsibility of selling lies with the brand manager or the product manager.
I present to you a series of articles in which I will take you through the complete process of performing sales forecasting.
In this article, which is the first of this series, I will introduce to you the idea of Sales Forecasting. Further, I will explain to you what is a model and what are the dependent and independent variables in a model.
I will also be giving you the dataset for download, the one which I will be using to demonstrate the sales forecasting methods.
This article is an introduction to all of the amazing things that we will be doing to get some practice of Marketing Analytics.
Let’s get started.

How does a Brand Manager ensure sales?
All the products out there won’t just get sold if you put them out in the market and don’t tell anyone about it. The success of products is determined not only by how good the product is but also how well the benefits of those products have been communicated to the people.
That’s why one advertises. You need to advertise your product to get the word out in the market.
Second, once the people know about the product they would have certain queries and objections. More people would ask for the product at your showrooms.
There, your sales team needs to build a relationship with the potential customers, clear their doubts and answer their objections.
Eventually, the sales team will convert them to make them customers. And there is some sales effort that goes into doing that.
You as a brand manager might want to give out certain sales incentives to the salesmen. Also, since your product is an environmentally friendly product, you might also want to sponsor certain ‘Go-green’ events that are coming up.
You also have spent a certain amount of money on personal selling. All of these, the sales incentive, sponsorships, and personal selling are a part of Sales Promotions Expenditure.
So, here’s what it is.
You, as the brand manager, in this case, have two levers that you can pull in order to affect the sales outcome – advertisement and sales promotions.
In fact, there are more than just these two operations that a Brand Manager does, but for the purpose of this article, we shall stick to these two.
Now, a general sense of business suggests that the more you spend on advertising and sales promotion, higher would be the sales.
Let’s have a look at why sales forecasting a crucial part of a brand managers responsibility.
What is Sales Forecasting?
You could define Sales forecasting as
This estimation is based on an extrapolation of the sales data of the previous quarters and previous years.
The data required to perform the sales forecasting process is the actual sales data from the past few quarters. This becomes the dependent variable – i.e. the variable that is dependent upon the certain things that we do.
What are these things that we do which affect the sales?
We discussed those above already.
These are the advertising and sales promotion expenditures which become our independent variables.
It would make sense if you begin to think it this way. The independent variables do not change as a result of a change of any other variable in the model. These are the inputs that we give to affect the sales.
A small example is this equation:
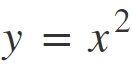
Here, y is the dependent variable which is dependent on the value of x that we will input. And this entire equation is our model. So if we wish to see a particular value of y, we know that we need to adjust the value of x to see that value.
Therefore, the independent variables are the levers that we pull and control in order to see a change in sales data.
Now, the purpose of sales forecasting is not only to set the sales target for the sales team. It also helps us setting a benchmark to evaluate the sales performance.

So, you can know whether the sales have underperformed or overachieved the sales based on what would have been the normal sales for this quarter.
Marketing Analytics for accurate Sales Forecasting
This estimation of sales and therefore this exercise of sales forecasting comes under the ambit of Marketing Analytics.
Through Marketing Analytics, certain analytical and statistical tools help us in performing the sales forecasting exercise.
The sales forecasting tools that we will use (MS Excel and SPSS) will analyze the past sales and expenditure data to develop a model.
As I explained above, a model is nothing but a mathematical equation (like y = x^2) that helps us explain the relationship between the dependent and the independent variable.
In our case, MS Excel or SPSS gives us a model or a sales forecast formula that will not only tell us the last quarter’s sales when we enter that quarter’s ad and sales promotion expenditure data.
But it will also use the same equation to tell us what the future sales will be for a given set of ad and sales promotion expenditure.
In the next article of this series, we will use a sales forecast example excel to apply an analytical technique called Linear Regression to see how accurately it will help us predict the future sales.
Further, in the subsequent articles, we will also see how Linear Regression is not always the best technique to predict sales in most of the cases. Therefore, we will have a look at the methods of Curve Estimation to get the most accurate sales forecasting model.
Before, I close this introductory article, here’s a little introduction of the dataset that I will be using for this series of articles.
Sales Forecasting Dataset
The dataset that I am going to use for this article is the one passed on to me by my professor of Marketing Analytics, the well-respect Prof. Prantosh Banerjee. Prof. Banerjee is an IIM Calcutta alumni and has been teaching Marketing Analytics, Consumer Behaviour, Market Research and Pricing at IIM Ahmedabad, IIM Udaipur and a few other B-schools.
You can download the dataset from here.
Download it and save it so that you can perform the linear regression and other analytical processes that I will take you through in the next few articles.
Here is a quick view of the dataset that you have with you.
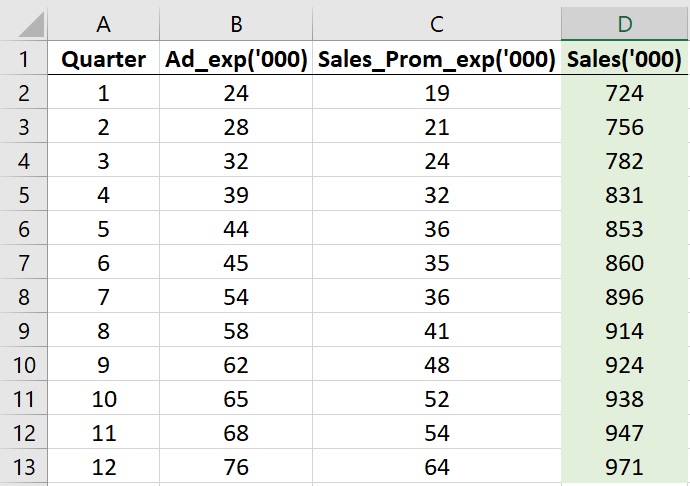
The dataset which I am using gives the final Sales for the last 12 quarters (column D).
In columns B and C, it also gives how much has my Advertisement and Sales Promotion Expenditure been.
These are my control variables. Because I could control how much I would want to spend on them.
Here’s a summary of the excel:
Column B – Advertisements – gives the amount spent on advertising in each quarter
Column C – Sales Promotion – tells the amount spent on sales promotions, sales training, and sales team incentives over the same period.
Column D – Actual Sales – tell the actual sales that happened in that
What next?
We are done with getting acquainted with the sales forecasting objective. We need to be predicting the sales for a given value of Advertisement expenditure and Sales Promotion expenditure.
This means, we need to develop a model, an equation, that satisfies (almost perfectly) the historical data that we have. Since it satisfies the existing data closely we can be sure that it would accurately predict the future sales data as well.
In the next article, we take a look at Linear Regression for Sales Forecasting.






Looking for the link to the next article!